Abstract
Research Article
Low sensitivity of the careHPV™ Assay for detection of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in cervical samples from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Kenyan women
Brown DR*, Titus M, Ermel A, Moormann A, Cu-Uvin S, Orang’o O, Tonui P, Chelimo K, Rosen B, Itsura P, Muthoka K, Loehrer P and Ong’echa JM
Published: 30 January, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-005
Background: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection causes cervical cancer (CC), a common malignancy among Kenyan women. New CC screening methods rely on oncogenic HPV (“high-risk”, or HR-HPV) detection, but most have not been evaluated in swabs from Kenyan women.
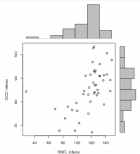
Methods: HPV typing was performed on 155 cervical swabs from Kenyan women using the Roche Linear Array® (LA) and careHPV™ (careHPV) assays. Detection of 14 oncogenic HPV types in careHPV assay was compared to LA results.
Results: Compared to LA, sensitivity and specificity of careHPV assay was 53.0% and 80.9%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of careHPV in swabs from women with cervical dysplasia was 74.1% and 65.2%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of careHPV in swabs from HIV-infected women was 55.9% and of 96.4%, respectively. Overall agreements of careHPV assay with LA was substantial.
Conclusion: The results for careHPV assay are promising for oncogenic HPV detection in Kenyan women. The low sensitivity of careHPV for detection of HR-HPV could limit it’s benefit as a screening tool. Thus, a full clinical validation study is highly desirable before the careHPV assay can be accepted for cervical cancer screening.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001006 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68: 394-424. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30207593
- zur Hausen H. Papillomavirus infections--a major cause of human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996; 1288: F55-F78. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8876633
- Bosch FX, de Sanjose S. Chapter 1: Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer--burden and assessment of causality. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2003; 31: 3-13. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12807939
- Munoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjose S, Herrero R, Castellsague X, et al. Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348: 518-527. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12571259
- Cronje HS. Screening for cervical cancer in developing countries. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2004; 84: 101-108. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14871510
- Vedantham H, Silver MI, Kalpana B, Rekha C, Karuna BP, et al. Determinants of VIA (Visual Inspection of the Cervix After Acetic Acid Application) positivity in cervical cancer screening of women in a peri-urban area in Andhra Pradesh, India. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010; 19: 1373-1380. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2913449/
- An Y, Shi X, Tang X, Wang Y, Shen F, et al. Aflatoxin B1 Induces Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Autophagy and Extracellular Trap Formation in Macrophages. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017; 7: 53. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5322174/
- Raifu AO, El-Zein M, Sangwa-Lugoma G, Ramanakumar A, Walter SD, et al. Determinants of Cervical Cancer Screening Accuracy for Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (VIA) and Lugol's Iodine (VILI) Performed by Nurse and Physician. PLoS One. 2017; 12: e0170631. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28107486
- El-Zein M, Richardson L, Franco EL. Cervical cancer screening of HPV vaccinated populations: Cytology, molecular testing, both or none. J Clin Virol. 2016; 76 Suppl 1: S62-S68. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26631958
- Ying H, Jing F, Fanghui Z, Youlin Q, Yali H. High-risk HPV nucleic acid detection kit-the careHPV test -a new detection method for screening. Sci Rep. 2014; 4: 4704. PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24736475
- Arney A, Bennett KM. Molecular Diagnostics of Human Papillomavirus. Lab Medicine. 2010; 41: 523-530.
- Brown DR, Shew ML, Qadadri B, Neptune N, Vargas M, et al. A longitudinal study of genital human papillomavirus infection in a cohort of closely followed adolescent women. J Infect Dis. 2005; 191: 182-192. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15609227
- Buderer NM. Statistical methodology: I. Incorporating the prevalence of disease into the sample size calculation for sensitivity and specificity. Acad Emerg Med. 1996; 3: 895-900. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8870764
- McGinn T, Wyer PC, Newman TB, Keitz S, Leipzig R, et al. Tips for learners of evidence-based medicine: 3. Measures of observer variability (kappa statistic). CMAJ. 2004; 171: 1369-1373. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15557592
- Manga MM, Fowotade A, Abdullahi YM, El-Nafaty AU, Adamu DB. Epidemiological patterns of cervical human papillomavirus infection among women presenting for cervical cancer screening in North-Eastern Nigeria. Infect Agent Cancer. 2015; 10: 39. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26435733
- Ngou J, Gilham C, Omar T, Goumbri-Lompo O, Doutre S, et al. Comparison of analytical and clinical performances of the digene HC2 HPV DNA assay and the INNO-LiPA HPV genotyping assay for detecting high-risk HPV infection and cervical neoplasia among HIV-positive African women. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015; 68: 162-168. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25394189
- Segondy M, Kelly H, Magooa MP, Djigma F, Ngou J, et al. Performance of careHPV for detecting high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia among women living with HIV-1 in Burkina Faso and South Africa: HARP study. Br J Cancer. 2016; 115: 425-430. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27434037
- Obiri-Yeboah D, Adu-Sarkodie Y, Djigma F, Akakpo K, Aniakwa-Bonsu E, et al. Options in human papillomavirus (HPV) detection for cervical cancer screening: comparison between full genotyping and a rapid qualitative HPV-DNA assay in Ghana. Gynecol Oncol Res Pract. 2017; 4: 5. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28270915
Similar Articles
-
Antiviral activity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves ethanolic extract on herpes viruses infectionMahmoud Huleihel*,Aya Abu-Jafar. Antiviral activity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves ethanolic extract on herpes viruses infection. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001001; 1: 001-009
-
Unveiling the gut virome in human health and diseasesTao Zuo*. Unveiling the gut virome in human health and diseases. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001002; 2: 001-003
-
Determine seroprevalence and associated risk factors of HBV infection among pregnant women and it relationship with blood transfusion at Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, SomalilandAbdullah Al-Mamari*. Determine seroprevalence and associated risk factors of HBV infection among pregnant women and it relationship with blood transfusion at Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, Somaliland. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001003; 3: 001-009
-
A model of the 2014 Ebola virus: Evidence of West AfricaNadhem Selmi*. A model of the 2014 Ebola virus: Evidence of West Africa. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001004; 3: 010-015
-
Frequency of cytomegalovirus infection in children with Nephrotic SyndromeDoaa Mohammed Youssef*,Mohammed Hassan Mohammed,Eman Mohammed EL-Behaidy,Asmaa EL-Sayed Abo-warda1. Frequency of cytomegalovirus infection in children with Nephrotic Syndrome. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001005; 3: 016-020
-
Low sensitivity of the careHPV™ Assay for detection of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in cervical samples from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Kenyan womenBrown DR*,Titus M,Ermel A,Moormann A,Cu-Uvin S,Orang’o O,Tonui P,Chelimo K,Rosen B,Itsura P,Muthoka K,Loehrer P,Ong’echa JM. Low sensitivity of the careHPV™ Assay for detection of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in cervical samples from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Kenyan women. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001006; 4: 001-005
-
Rubella infection: Advances and challenges in the diagnosis and prevention of Congenital Rubella SyndromeAmélia Nkutxi Vueba*,Maria do Céu Sousa. Rubella infection: Advances and challenges in the diagnosis and prevention of Congenital Rubella Syndrome. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001007; 4: 006-013
-
Pseudoephedrine protects mice from infection of H1N1 virusZhongping Wu*,Li Deng,Chengzhi Chu,Xiaoyin Chen*. Pseudoephedrine protects mice from infection of H1N1 virus. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001008; 4: 014-020
-
Hypothesis about pathogenic action of Sars-COV-2Del Prete Salvatore*,Marasco Daniela,Sabetta Rosalaura. Hypothesis about pathogenic action of Sars-COV-2. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001009; 4: 021-022
-
Vitamin D produce antibodies in pandemic response to gripal viruses? A critical analysisEliza Miranda Ramos*,Francisco José Mendes dos Reis,Hugo Vieira Ramos,Igor Domingos de Souza,Liliane de Mello Santos Bochenek,Alessandro Carvalho da Fonseca,Valter Aragão do Nascimento. Vitamin D produce antibodies in pandemic response to gripal viruses? A critical analysis. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001010; 4: 023-026
Recently Viewed
-
Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical TrialAnders Wänman*, Susanna Marklund, Negin Yekkalam. Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001046; 9: 001-008
-
Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with DiabetesHakob Khachatryan, Emma Boshnaghyan, Sevak Papoyan, Gagik Hakobyan*. Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with Diabetes. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001047; 9: 009-014
-
Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip ImplantsShekufeh Shafeie*. Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip Implants. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001048; 9: 015-018
-
Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and XenograftMohammad Azimzadeh, Farzad Esmaeili, Narges Bayat, Kasra Rahimipour, Amir Ebrahimpour Tolouei*. Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and Xenograft. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001049; 9: 019-022
-
Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the JawsAbdulhamit Taha Koca,Mustafa Bayhan,Yunus Ayberk Demir,Ayse Zeynep Zengin*. Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001050; 9: 023-031
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."