Abstract
Review Article
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms and the development of COVID-19: a review of the literature
Adrhyan Araújo da Silva Oliveira, Ana Maisa Passos da Silva, Jackson Alves da Silva Queiroz, Paulo Ricardo Freitas de Souza, Juan Miguel Villalobos Salcedo and Deusilene Souza Vieira*
Published: 28 April, 2022 | Volume 6 - Issue 1 | Pages:
SARS-CoV-2 is a virus that has a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome that encodes 4 structural proteins, the main one being the S protein (Spike) responsible for mediating with ACE2 and TMPRSS2 for entry into the host cell. The study of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 can elucidate their possible intervention in the action of the protein, its activity, and the gene expression of encoding these enzymes, which may increase susceptibility to viral infection. From this, literature searches were carried out until December 2021, listing 11,820 publications for literary analysis on the described genetic variations of these protein structures, as well as their relation and influence on the pathology. It was possible to conclude that there is a great influence exerted by genetic variability in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 increasing the ability of the virus to bind to the host cell and the development of COVID-19 with complications.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001044 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Polymorphisms; ACE2; TMPRSS2; COVID-19; Susceptibility
References
- Muralidar S, Ambi SV, Sekaran S, Krishnan UM. The emergence of COVID-19 as a global pandemic: Understanding the epidemiology, immune response and potential therapeutic targets of SARS-CoV-2. Biochimie. 2020 Dec;179:85-100. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.09.018. Epub 2020 Sep 22. PMID: 32971147; PMCID: PMC7505773.
- Arya R, Kumari S, Pandey B, Mistry H, Bihani SC, Das A, Prashar V, Gupta GD, Panicker L, Kumar M. Structural insights into SARS-CoV-2 proteins. J Mol Biol. 2021 Jan 22;433(2):166725. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.11.024. Epub 2020 Nov 24. PMID: 33245961; PMCID: PMC7685130.
- Singh H, Choudhari R, Nema V, Khan AA. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms in various diseases with special reference to its impact on COVID-19 disease. Microb Pathog. 2021 Jan;150:104621. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104621. Epub 2020 Dec 2. PMID: 33278516; PMCID: PMC7709597.
- Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Mar;19(3):141-154. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Erratum in: Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 May;20(5):315. PMID: 33024307; PMCID: PMC7537588.
- Altiok D, Savci EZ, Özkara B, Alkan K, Namdar DS, Tunçer G, Kilinç BR, Suiçmez E, Çetin G, Ünal S, Dönmüş B, Karagülleoğlu ZY, Uncuoğlu DB, Tekeli C, Mendi HA, Bengi VU, Cengiz Seval G, Kiliç P, Güneş Altuntaş E, Demir-Dora D. Host variations in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Turk J Biol. 2021 Aug 30;45(4):404-424. doi: 10.3906/biy-2104-67. PMID: 34803443; PMCID: PMC8573834.
- Soleimanpour S, Yaghoubi A. COVID-19 vaccine: where are we now and where should we go? Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021 Jan;20(1):23-44. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2021.1875824. Epub 2021 Feb 17. PMID: 33435774; PMCID: PMC7898300.
- Dong M, Zhang J, Ma X, Tan J, Chen L, Liu S, Xin Y, Zhuang L. ACE2, TMPRSS2 distribution and extrapulmonary organ injury in patients with COVID-19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110678. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110678. Epub 2020 Aug 24. PMID: 32861070; PMCID: PMC7444942.
- Gomes CP, Fernandes DE, Casimiro F, da Mata GF, Passos MT, Varela P, Mastroianni-Kirsztajn G, Pesquero JB. Cathepsin L in COVID-19: From Pharmacological Evidences to Genetics. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Dec 8;10:589505. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.589505. PMID: 33364201; PMCID: PMC7753008.
- Glotov OS, Chernov AN, Scherbak SG, Baranov VS. Genetic Risk Factors for the Development of COVID-19 Coronavirus Infection. Russ J Genet. 2021;57(8):878-892. doi: 10.1134/S1022795421080056. Epub 2021 Aug 30. PMID: 34483599; PMCID: PMC8404752.
- Lanjanian H, Moazzam-Jazi M, Hedayati M, Akbarzadeh M, Guity K, Sedaghati-Khayat B, Azizi F, Daneshpour MS. SARS-CoV-2 infection susceptibility influenced by ACE2 genetic polymorphisms: insights from Tehran Cardio-Metabolic Genetic Study. Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 15;11(1):1529. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80325-x. PMID: 33452303; PMCID: PMC7810897.
- Zlacká J, Stebelová K, Zeman M, Herichová I. Interactions of renin-angiotensin system and COVID-19: the importance of daily rhythms in ACE2, ADAM17 and TMPRSS2 expression. Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 16;70(S2):S177-S194. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934754. PMID: 34913351; PMCID: PMC8884363.
- Katopodis P, Randeva HS, Spandidos DA, Saravi S, Kyrou I, Karteris E. Host cell entry mediators implicated in the cellular tropism of SARS‑CoV‑2, the pathophysiology of COVID‑19 and the identification of microRNAs that can modulate the expression of these mediators (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022 Feb;49(2):20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5075. Epub 2021 Dec 22. PMID: 34935057; PMCID: PMC8722767.
- Hubacek JA. Effects of selected inherited factors on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 progression. Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 16;70(S2):S125-S134. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934730. PMID: 34913347; PMCID: PMC8884368.
- Parmar MS. TMPRSS2: An Equally Important Protease as ACE2 in the Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021 Nov;96(11):2748-2752. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Jul 15. PMID: 34736607; PMCID: PMC8279956.
- Takeda M. Proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Microbiol Immunol. 2022 Jan;66(1):15-23. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12945. Epub 2021 Oct 12. PMID: 34561887; PMCID: PMC8652499.
- Kadam SB, Sukhramani GS, Bishnoi P, Pable AA, Barvkar VT. SARS-CoV-2, the pandemic coronavirus: Molecular and structural insights. J Basic Microbiol. 2021 Mar;61(3):180-202. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202000537. Epub 2021 Jan 18. PMID: 33460172; PMCID: PMC8013332.
- V'kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H, Thiel V. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Mar;19(3):155-170. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6. Epub 2020 Oct 28. PMID: 33116300; PMCID: PMC7592455.
- Velusamy P, Kiruba K, Su CH, Arun V, Anbu P, Gopinath SCB, Vaseeharan B. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Site-specific breakpoints for the development of COVID-19 vaccines. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2021 Dec;33(8):101648. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2021.101648. Epub 2021 Oct 19. PMID: 34690467; PMCID: PMC8523302.
- Morgun AV, Salmin VV, Boytsova EB, Lopatina OL, Salmina AB. Molecular Mechanisms of Proteins - Targets for SARS-CoV-2 (Review). Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021;12(6):98-108. doi: 10.17691/stm2020.12.6.11. Epub 2020 Dec 28. PMID: 34796023; PMCID: PMC8596231.
- Peng J, Sun J, Zhao J, Deng X, Guo F, Chen L. Age and gender differences in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expressions in oral epithelial cells. J Transl Med. 2021 Aug 19;19(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03037-4. PMID: 34412632; PMCID: PMC8374411.
- Viveiros A, Gheblawi M, Aujla PK, Sosnowski DK, Seubert JM, Kassiri Z, Oudit GY. Sex- and age-specific regulation of ACE2: Insights into severe COVID-19 susceptibility. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Mar;164:13-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.11.003. Epub 2021 Nov 11. PMID: 34774871; PMCID: PMC8582230.
- Xu F, Gao J, Bergmann S, Sims AC, Ashbrook DG, Baric RS, Cui Y, Jonsson CB, Li K, Williams RW, Schughart K, Lu L. Genetic Dissection of the Regulatory Mechanisms of Ace2in the Infected Mouse Lung. Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 8;11:607314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607314. PMID: 33488611; PMCID: PMC7819859.
- Clarke SA, Abbara A, Dhillo WS. Impact of COVID-19 on the Endocrine System: A Mini-review. Endocrinology. 2022 Jan 1;163(1):bqab203. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab203. PMID: 34543404; PMCID: PMC8500009.
- Abdi A, AlOtaiby S, Badarin FA, Khraibi A, Hamdan H, Nader M. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with cardiomyocytes: Insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms of cardiac injury and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Feb;146:112518. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112518. Epub 2021 Dec 9. PMID: 34906770; PMCID: PMC8654598.
- Deng H, Yan X, Yuan L. Human genetic basis of coronavirus disease 2019. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Sep 20;6(1):344. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00736-8. PMID: 34545062; PMCID: PMC8450706.
- Agolli A, Yukselen Z, Agolli O, Patel MH, Bhatt KP, Concepcion L, Halpern J, Alvi S, Abreu R. SARS-CoV-2 effect on male infertility and its possible pathophysiological mechanisms. Discoveries (Craiova). 2021 Jun 30;9(2):e131. doi: 10.15190/d.2021.10. PMID: 34816001; PMCID: PMC8605861.
- Ragia G, Manolopoulos VG. Assessing COVID-19 susceptibility through analysis of the genetic and epigenetic diversity of ACE2-mediated SARS-CoV-2 entry. Pharmacogenomics. 2020;21(18):1311–1329.
- Hasan MR, Ahmad MN, Dargham SR, Zayed H, Al Hashemi A, Ngwabi N, Perez Lopez A, Dobson S, Abu Raddad LJ, Tang P. Nasopharyngeal Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 in Children within SARS-CoV-2-Infected Family Clusters. Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0078321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00783-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. PMID: 34730438; PMCID: PMC8567246.
- Hörnich BF, Großkopf AK, Schlagowski S, Tenbusch M, Kleine-Weber H, Neipel F, Stahl-Hennig C, Hahn AS. SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV Spike-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion Differ in Their Requirements for Receptor Expression and Proteolytic Activation. J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e00002-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00002-21. PMID: 33608407; PMCID: PMC8104116.
- Hossain MS, Tonmoy MIQ, Fariha A, Islam MS, Roy AS, Islam MN, Kar K, Alam MR, Rahaman MM. Prediction of the Effects of Variants and Differential Expression of Key Host Genes ACE2, TMPRSS2, and FURINin SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis: An In Silico Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021 Oct 26;15:11779322211054684. doi: 10.1177/11779322211054684. PMID: 34720581; PMCID: PMC8554545.
- Tarek M, Abdelzaher H, Kobeissy F, El-Fawal HAN, Salama MM, Abdelnaser A. Bioinformatics Analysis of Allele Frequencies and Expression Patterns of ACE2, TMPRSS2 and FURIN in Different Populations and Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2. Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 5;12(7):1041. doi: 10.3390/genes12071041. PMID: 34356057; PMCID: PMC8303858.
- Ravaioli S, Tebaldi M, Fonzi E, Angeli D, Mazza M, Nicolini F, Lucchesi A, Fanini F, Pirini F, Tumedei MM, Cerchione C, Viale P, Sambri V, Martinelli G, Bravaccini S. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Potential Involvement in Genetic Susceptibility to SARS-COV-2 in Cancer Patients. Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720968749. doi: 10.1177/0963689720968749. PMID: 33108902; PMCID: PMC7593730.
- Jeon S, Blazyte A, Yoon C, Ryu H, Jeon Y, Bhak Y, Bolser D, Manica A, Shin ES, Cho YS, Kim BC, Ryoo N, Choi H, Bhak J. Regional TMPRSS2 V197M Allele Frequencies Are Correlated with COVID-19 Case Fatality Rates. Mol Cells. 2021 Sep 30;44(9):680-687. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.2249. PMID: 34588322; PMCID: PMC8490206.
- Lee D. The impact of COVID-19 on human reproduction and directions for fertility treatment during the pandemic. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2021 Dec;48(4):273-282. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2021.04504. Epub 2021 Nov 26. PMID: 34875734; PMCID: PMC8651760.
- Nayak B, Lal G, Kumar S, Das CJ, Saraya A, Shalimar. Host Response to SARS-CoV2 and Emerging Variants in Pre-Existing Liver and Gastrointestinal Diseases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 25;11:753249. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.753249. PMID: 34760721; PMCID: PMC8573081.
- Generali M, Kehl D, Wanner D, Okoniewski MJ, Hoerstrup SP, Cinelli P. Heterogeneous expression of ACE2 and TMPRRS2 in mesenchymal stromal cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan;26(1):228-234. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17048. Epub 2021 Nov 24. PMID: 34821008; PMCID: PMC8742235.
- Huang Z, Do DV, Beh D, Lee CK, Yan B, Foo R, Tambyah PA. Effects of acute severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection on male hormone profile, ACE2and TMPRSS2 expression, and potential for transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in semen of Asian men. F S Sci. 2022 Feb;3(1):29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.xfss.2021.11.003. Epub 2021 Nov 20. PMID: 34841282; PMCID: PMC8604798.
- Jeong M, Ocwieja KE, Han D, Wackym PA, Zhang Y, Brown A, Moncada C, Vambutas A, Kanne T, Crain R, Siegel N, Leger V, Santos F, Welling DB, Gehrke L, Stankovic KM. Direct SARS-CoV-2 infection of the human inner ear may underlie COVID-19-associated audiovestibular dysfunction. Commun Med (Lond). 2021;1(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s43856-021-00044-w. Epub 2021 Oct 29. PMID: 34870285; PMCID: PMC8633908.
- Sapkota D, Sharma S, Søland TM, Braz-Silva PH, Teh MT. Expression profile of SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry proteins in normal oral mucosa and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022 Feb;8(1):117-122. doi: 10.1002/cre2.510. Epub 2021 Nov 2. PMID: 34726347; PMCID: PMC8653086.
Figures:
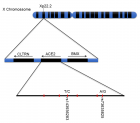
Figure 1
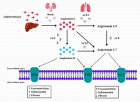
Figure 2
Figure 3
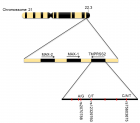
Figure 4
Similar Articles
-
The Psychology of the Common Cold and Influenza: Implications for COVID-19Andrew P Smith*. The Psychology of the Common Cold and Influenza: Implications for COVID-19. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001011; 4: 027-031
-
Yemen is free of COVID-19Hussein O Kadi*. Yemen is free of COVID-19. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001012; 4: 032-033
-
Exploring pathophysiology of COVID-19 infection: Faux espoir and dormant therapeutic optionsVinod Nikhra*. Exploring pathophysiology of COVID-19 infection: Faux espoir and dormant therapeutic options. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001013; 4: 034-040
-
COVID-19: Targeting the cytokine storm via cholinergic anti-inflammatory (Pyridostigmine)Ahmed H Osman*. COVID-19: Targeting the cytokine storm via cholinergic anti-inflammatory (Pyridostigmine). . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001014; 4: 041-046
-
Identifying patterns in COVID-19: Morbidity, recovery and the aftermathVinod Nikhra*. Identifying patterns in COVID-19: Morbidity, recovery and the aftermath. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001016; 4: 056-064
-
Role of nanotechnology in diagnosing and treating COVID-19 during the PandemicAbdul Baset*,Abdul Waris,Muhammad Ali,Atta Ullah Khan,Asmat Ali. Role of nanotechnology in diagnosing and treating COVID-19 during the Pandemic. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001017; 4: 065-070
-
COVID-19: The possible medical strategiesMohamed SA Mohamed*. COVID-19: The possible medical strategies. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001018; 4: 071-075
-
Inhaled statins to combat COVID-19 – prophylactic and treatment approachArchana P Iyer*,Maryam A Al-Ghamdi. Inhaled statins to combat COVID-19 – prophylactic and treatment approach. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001020; 4: 079-080
-
A Comprehensive review on genomic diversity and epidemiology of COVID-19Zeshan Haider Raza*,Muhammad Ahmed Ihsan,Sahrish Khan,Haroon Zafar,Tayyaba Rehman. A Comprehensive review on genomic diversity and epidemiology of COVID-19. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001021; 4: 081-095
-
The expected second wave of COVID-19Madiha Asghar*,Misbahud Din. The expected second wave of COVID-19. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001024; 4: 109-110
Recently Viewed
-
Advancing Forensic Approaches to Human Trafficking: The Role of Dental IdentificationAiswarya GR*. Advancing Forensic Approaches to Human Trafficking: The Role of Dental Identification. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001076; 9: 025-028
-
Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in EvaluationKelly Kearse*,Frank Ligaj. Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in Evaluation. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001068; 8: 078-088
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Toxicity and Phytochemical Analysis of Five Medicinal PlantsJohnson-Ajinwo Okiemute Rosa*, Nyodee, Dummene Godwin. Toxicity and Phytochemical Analysis of Five Medicinal Plants. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001054; 8: 029-040
-
Antibacterial Screening of Lippia origanoides Essential Oil on Gram-negative BacteriaRodrigo Marcelino Zacarias de Andrade, Bernardina de Paixão Santos, Roberson Matteus Fernandes Silva, Mateus Gonçalves Silva*, Igor de Sousa Oliveira, Sávio Benvindo Ferreira, Rafaelle Cavalcante Lira. Antibacterial Screening of Lippia origanoides Essential Oil on Gram-negative Bacteria. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001053; 8: 024-028.
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."