Abstract
Research Article
Mass Serological Screening in the Armed Forces Using the Serum-Pooling Method. Analytical Evaluation of the Chemiluminescence Method
Abi R*, Ameur O, Hassine S, Chanhih N, Ouannass S, Goura H, Eddaif KH, Elkochri S, Aadi Y, Elbenaissi Y, Tagajdid MR, Elannaz H, Laraqui A, Elmchichi B, Touil N, Kasouati J, Elouennass M, Ennibi K and Lahlou IA
Published: 18 February, 2025 | Volume 9 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-004
Mass serological screening in the Armed Forces involves detecting serological markers of
chronic infections, particularly viral hepatitis B and C, syphilis, and HIV among young military
recruits. The objective of this study is to evaluate the analytical performance of the
chemiluminescence technique (CMIA-Architect i2000 SR) in mass serological screening using the serum-pooling method at the virology laboratory of the Mohammed V Military Teaching Hospital.
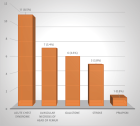
Samples with known serological results (positive/negative) were grouped into pools of different sizes (2, 5, 10, and 15 sera). These pools were tested using chemiluminescence (CMIA-Architect i2000 SR). A cost analysis was conducted to assess potential savings based on seroprevalence and pool size.
Results showed that the pooling method maintained 100% specificity. Overall sensitivities for detecting positive samples were 93.1% for HBV, 83.33% for HCV, and 86.36% for HIV. Positive and negative predictive values were high for all three viral markers, highlighting the reliability of the pooling method. Additionally, this approach generated significant cost savings, ranging from 46% to 80%.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the solid analytical performance of the chemiluminescence technique (CMIA-Architect i 2000 SR) using the serum-pooling method for detecting HBV, HCV, and HIV serological markers in low-seroprevalence regions.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001062 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Screening; Pooling; Chemiluminescence
References
- Abdalhamid B, Bilder CR, McCutchen EL, Hinrichs SH, Koepsell SA, Iwen PC. Assessment of specimen pooling to conserve SARS CoV-2 testing resources. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020;153(6):715-718. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqaa064
- Dorfman R. The detection of defective members of large populations. Ann Math Statist. 1943;14(4):436-440. Available from: https://www.medicine.mcgill.ca/epidemiology/hanley/bios601/Likelihood/Dorfman1943PooledTests.pdf.
- Cunningham R, Northwood JL, Kelly CD, Boxall EH, Andrews NJ. Routine antenatal screening for hepatitis B using pooled sera: validation and review of 10 years experience. J Clin Pathol. 1998;51(5):392-395. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.51.5.392
- Novack L, Sarov B, Goldman-Levi R, Yahalom V, Safi J, Soliman H, et al. Impact of pooling on accuracy of hepatitis B virus surface antigen screening of blood donations. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2008;102(8):787-792. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.04.005
- Dinesha TR, Boobalan J, Sivamalar S, Subashini D, Solomon SS, Murugavel KG, et al. Occult HBV infection in HIV-infected adults and evaluation of pooled NAT for HBV. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25(6):718-723. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12858
- Liu P, Shi Z, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Shu H, Zhang X. A prospective study of a serum-pooling strategy in screening blood donors for antibody to hepatitis C virus. Transfusion. 1997;37(7):732-736. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1537-2995.1997.37797369450.x
- Rabenau H, Schütz R, Berger A, Doerr HW, Weber B. How accurate is serologic testing of plasma pools for hepatitis B virus surface antigen, anti-human immunodeficiency virus 1 and 2, and anti-hepatitis C virus? Transfus Med Hemother. 1996;23(3):124-130. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1159/000223281
- Emmanuel JC, Bassett MT, Smith HJ, Jacobs JA. Pooling of sera for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing: an economical method for use in developing countries. J Clin Pathol. 1988;41(5):582-585. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.41.5.582
- McMahon EJ, Fang C, Layug L, Sandler SG. Pooling blood donor samples to reduce the cost of HIV-1 antibody testing. Vox Sang. 1995;68(4):215-219. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1423-0410.1995.tb02575.x
- Saleh RM, Farouk AM, Anani M, Attia FM. Validation of specimen pooling versus individual samples for screening of viral markers and syphilis in blood bag strategy: Single-center study. Egypt J Hosp Med. 2023;90:757-762. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21608/ejhm.2023.279928
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Determine seroprevalence and associated risk factors of HBV infection among pregnant women and it relationship with blood transfusion at Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, SomalilandAbdullah Al-Mamari*. Determine seroprevalence and associated risk factors of HBV infection among pregnant women and it relationship with blood transfusion at Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, Somaliland. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001003; 3: 001-009
-
Low sensitivity of the careHPV™ Assay for detection of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in cervical samples from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Kenyan womenBrown DR*,Titus M,Ermel A,Moormann A,Cu-Uvin S,Orang’o O,Tonui P,Chelimo K,Rosen B,Itsura P,Muthoka K,Loehrer P,Ong’echa JM. Low sensitivity of the careHPV™ Assay for detection of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus in cervical samples from HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Kenyan women. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001006; 4: 001-005
-
Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in SenegalMoustapha Mbow*,Ibrahima Diallo,Mamadou Diouf,Marouba Cissé#,Moctar Gningue#,Aminata Mboup,Nafissatou Leye,Gora Lo,Yacine Amet Dia,Abdou Padane,Djibril Wade,Josephine Khady Badiane,Oumar Diop,Aminata Dia,Ambroise Ahouidi,Doudou George Massar Niang,Babacar Mbengue,Maguette Dème Sylla Niang,Papa Alassane Diaw,Tandakha Ndiaye Dieye,Badara Cisé,El Hadj Mamadou Mbaye,Alioune Dieye,Souleymane Mboup. Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in Senegal. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001041; 6: 001-006
-
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and centaurus variants induced lymphocytopenia: A multicenter clinical investigation on 118,561 cases across Pakistan during 2021-2022Rizwan Uppal,Muhammad Saad Uppal,Aftab Ahmad Khan,Umar Saeed*. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and centaurus variants induced lymphocytopenia: A multicenter clinical investigation on 118,561 cases across Pakistan during 2021-2022. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001047; 6: 034-037
-
Validating the ORACollect for the detection of cytomegalovirusAlanna N Gillespie, Richard Saffery, Andrew J Daley, Gregory Waller, Bowon Kim, Melissa Wake, Anna Czajko, Valerie Sung*. Validating the ORACollect for the detection of cytomegalovirus. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001053; 7: 007-010
-
Screening for BK Virus Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients at Mohamed V Military Teaching HospitalO Skalante, S Elkochri, FZ Adil, M Hachimi Idrissi, Y Aadi, Y Elbenaissi, A Bahadi, MR Tagajdid, H Elannaz, A Laraqui, B Elmchichi, N Touil, K Ennibi, I Lahlou Amine, R Abi*. Screening for BK Virus Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients at Mohamed V Military Teaching Hospital. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001058; 8: 024-025
-
Mass Serological Screening in the Armed Forces Using the Serum-Pooling Method. Analytical Evaluation of the Chemiluminescence MethodAbi R*,Ameur O,Hassine S,Chanhih N,Ouannass S,Goura H,Eddaif KH,Elkochri S,Aadi Y,Elbenaissi Y,Tagajdid MR,Elannaz H,Laraqui A,Elmchichi B,Touil N,Kasouati J,Elouennass M,Ennibi K,Lahlou IA. Mass Serological Screening in the Armed Forces Using the Serum-Pooling Method. Analytical Evaluation of the Chemiluminescence Method. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001062; 9: 001-004
Recently Viewed
-
Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical TrialAnders Wänman*, Susanna Marklund, Negin Yekkalam. Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001046; 9: 001-008
-
Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with DiabetesHakob Khachatryan, Emma Boshnaghyan, Sevak Papoyan, Gagik Hakobyan*. Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with Diabetes. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001047; 9: 009-014
-
Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip ImplantsShekufeh Shafeie*. Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip Implants. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001048; 9: 015-018
-
Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and XenograftMohammad Azimzadeh, Farzad Esmaeili, Narges Bayat, Kasra Rahimipour, Amir Ebrahimpour Tolouei*. Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and Xenograft. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001049; 9: 019-022
-
Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the JawsAbdulhamit Taha Koca,Mustafa Bayhan,Yunus Ayberk Demir,Ayse Zeynep Zengin*. Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001050; 9: 023-031
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."